Getting Started
Introduction
Atata Framework - C#/.NET web UI test automation full-featured framework based on Selenium WebDriver. It uses a fluent page object pattern; has a built-in logging system; contains a unique triggers functionality; has a set of ready-to-use components. One of the key ideas of the framework is to provide a simple and intuitive syntax for defining and using page objects. A page object implementation requires as less code as possible. You can describe a page object class without any methods and only have a set of properties marked with attributes representing page components.
The framework is completely open-source and hosted on GitHub as Atata Framework organization under the Apache License 2.0. All framework libraries are published and available as NuGet packages.
Concepts
The framework basically consists of the following concepts:
- AtataContext
- Configuration - use fluent builder and/or JSON config.
- Components
- Controls
- Page objects
- Control list
- Attributes
- Attributes of control search - basically, element locators,
like
[FindById],[FindByName],[FindByXPath], etc. - Trigger attributes - a functionality that is automatically executed in response to certain events on a particular component. For example, when a click on button occurs it may be defined that a wait should be executed.
- Behavior attributes - change the way how particular actions are executed.
For example, specify the click behavior for a specific button by adding
[ClickUsingScript]to perform the click using JavaScript, instead of defaultIWebElement.Click()way. - Settings attributes - set settings for control finding, culture, value format, etc.
- Attributes of control search - basically, element locators,
like
- Verification functionality
.Should.*- an assertion. For example:UserName.Should.Be("John")..ExpectTo.*- an expectation, which produces a warning..WaitTo.*- a waiting for a certain condition.
Packages
Atata Framework consists of a set of NuGet packages.
Main Packages
- Atata (GitHub | NuGet) - is a main package, which provides base and main functionality for web UI testing.
- Atata.Configuration.Json (GitHub | NuGet) - provides configuration through JSON files.
- Atata.WebDriverSetup (GitHub | NuGet) -
sets up browser drivers, e.g.
chromedriver,geckodriver, etc. Basically, it provides functionality similar to JavaWebDriverManager. - Atata.HtmlValidation (GitHub | NuGet) - adds HTML page validation to Atata using html-validate NPM package.
- Atata.Bootstrap (GitHub | NuGet) - contains a set of Atata components for Bootstrap Framework.
- Atata.KendoUI (GitHub | NuGet) - contains a set of Atata components for Kendo UI HTML Framework.
Additional Packages
- Atata.WebDriverExtras (GitHub | NuGet) - contains extension methods and other extra classes for Selenium WebDriver. Used by Atata.
- Atata.Cli (GitHub | NuGet) - provides an API for CLI.
- Atata.Cli.Npm (GitHub | NuGet) - provides an API for CLI of NPM.
- Atata.Cli.HtmlValidate (GitHub | NuGet) - provides an API for CLI of html-validate NPM package.
Installation
There are 2 options to create a project in Visual Studio for automated testing using Atata Framework.
Install via Atata Templates
To get started, install Atata Templates Visual Studio extension.
The extension provides the following templates:
- Project templates:
- Atata NUnit Basic Test Project (.NET 6)
- Atata NUnit Basic Test Project (.NET 8)
- Atata NUnit Advanced Test Project (.NET 6)
- Atata NUnit Advanced Test Project (.NET 8)
- Item templates:
- Atata Page Object
- Atata Base Page Object
- Atata Control
- Atata Trigger
- Atata NUnit Test Fixture
- Atata NUnit Base Test Fixture
Create Project
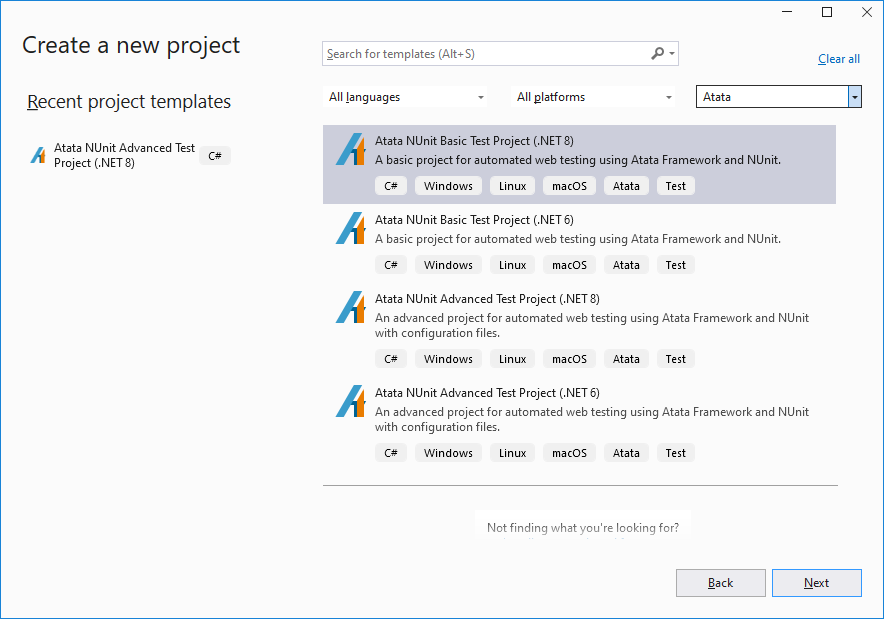
When extension is installed, you can create a project of one of Atata project types. In Visual Studio:
- Go to File/New/Project… or File/Add/New Project… (to add to existing solution).
- Type Atata into search box or choose Atata in “project types” drop-down.
- Choose template, e.g., Atata NUnit Advanced Test Project (.NET 8), and specify project name and location.
Project References
The project is created with NuGet package references:
- Atata
- Atata.WebDriverSetup
- Microsoft.NET.Test.Sdk
- NUnit
- NUnit3TestAdapter
- Atata.Configuration.Json (for advanced project)
- NLog (for advanced project)
Configuration
You don’t need to configure specific browser driver packages, as a project is by default configured to automatically download appropriate driver, by use of Atata.WebDriverSetup package.
In the created project you can specify your testing site base URL and appropriate driver in
SetUpFixture.cs or Atata.local.json class, depending on type of project (basic or advanced).
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.UseChrome()
.WithArguments("start-maximized")
.UseBaseUrl("https://atata.io/")
//...
{
"baseUrl": "https://atata.io/"
// Other environment specific configuration properties can be added here.
}
Just replace "https://atata.io/" string with your URL.
Test Fixtures
The created project also contains ready to use SampleTests.cs fixture, which can be either modified or removed:
namespace AtataUITests1;
public class SampleTests : UITestFixture
{
[Test]
public void SampleTest() =>
Go.To<OrdinaryPage>()
.PageTitle.Should.Contain("Atata");
}
Further test fixture classes are recommended to inherit from UITestFixture,
or just choose “Atata NUnit Test Fixture” item template in “Add New Item Window”.
Create Project Targeting Other .NET Version
- Create a project using one of the project templates: “Atata NUnit Basic Test Project (.NET 6)”, “Atata NUnit Advanced Test Project (.NET 6)”.
- Open project
.csprojfile. - Change the value of
<TargetFramework>tag fromnet6.0to the needed version.<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk"> <PropertyGroup> <TargetFramework>NET_VERSION</TargetFramework> <!-- ... --> </PropertyGroup> <!-- ... --> </Project>
Install via NuGet
It is a more custom approach to create Atata testing project. To get started just add Atata NuGet package to the project of Class Library (.NET Framework, .NET Core or .NET 5+) type in Visual Studio.
PM> Install-Package Atata
The Atata package depends on the following packages, which are added automatically:
You might also need to install Atata.WebDriverSetup package
for auto-setup of browser drivers, e.g. chromedriver, geckodriver, etc.
This is a recommended option.
Alternatively, you can install a driver package for specific browser:
Selenium.WebDriver.ChromeDriver,
Selenium.WebDriver.IEDriver,
etc.
But be aware to keep version synchronization of browser and driver.
You are also free to select any test engine framework: NUnit, Xunit, MSTest, SpecFlow, etc.
For .NET Core and .NET 5+ projects it is required also to add Microsoft.NET.Test.Sdk package to the project that contains tests (no matter NUnit, xUnit, MSTest, etc.).
NUnit Project Configuration
In addition to Atata NuGet package, add the following packages:
Then add 2 C# class files.
The first SetUpFixture class sets the global Atata configuration,
like which browser driver to use, basic URL, etc.
Then it sets up an appropriate driver executable for the browser to use.
SetUpFixture.cs
using Atata;
using NUnit.Framework;
namespace SampleApp.UITests;
[SetUpFixture]
public class SetUpFixture
{
[OneTimeSetUp]
public void GlobalSetUp()
{
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.UseChrome()
.WithArguments("start-maximized")
.UseBaseUrl("https://atata.io/")
.UseCulture("en-US")
.UseAllNUnitFeatures();
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration.AutoSetUpDriverToUse();
}
}
The second UITestFixture class is the base class for all test fixture classes that have UI tests.
It just starts an Atata session before the test run and closes it after the test is finished.
SetUpFixture.cs
using Atata;
using NUnit.Framework;
namespace SampleApp.UITests;
[TestFixture]
[Parallelizable(ParallelScope.Self)]
public class UITestFixture
{
[SetUp]
public void SetUp() =>
AtataContext.Configure().Build();
[TearDown]
public void TearDown() ==>
AtataContext.Current?.Dispose();
}
Xunit Project Configuration
Check out Xunit Atata sample project.
MSTest Project Configuration
Check out MSTest Atata sample project.
SpecFlow Project Configuration
Check out SpecFlow Atata sample project.
Usage
Lat’s create a simple test automation project example with a test for Sign In page.
Create Project
In Visual Studio create a project using Installation instructions.
Set Atata base URL to "https://demo.atata.io/" either in SetUpFixture.cs or Atata.local.json file.
Define Page Object Class
SignInPage.cs
namespace AtataDemo.UITests;
using _ = SignInPage;
[Url("signin")]
public class SignInPage : Page<_>
{
public TextInput<_> Email { get; private set; }
public PasswordInput<_> Password { get; private set; }
public Button<_> SignIn { get; private set; }
}
The aspects of the created page object:
[Url("signin")]- sets the relative URL of the page to be navigated to. Good for pages with static URLs.- Default search of
EmailandPasswordcontrols is performed by label. Can be changed/configured. - Default search of
SignInbutton is performed by its text.
Implement Test
SignInTests.cs
namespace AtataDemo.UITests;
[TestFixture]
public class SignInTests : UITestFixture
{
[Test]
public void SignIn() =>
Go.To<SignInPage>()
.Email.Type("admin@mail.com")
.Password.Type("abc123")
.SignIn.Click();
}
View Log
The above sample SignIn test generates the following log to NUnit output:
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1153 INFO Starting test: AtataDemo.UITests.SignInTests.SignIn
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1247 TRACE > Initialize AtataContext
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1264 TRACE - Set: BaseUrl=https://demo.atata.io/
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1275 TRACE - Set: ElementFindTimeout=5s; ElementFindRetryInterval=0.5s
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1277 TRACE - Set: WaitingTimeout=5s; WaitingRetryInterval=0.5s
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1278 TRACE - Set: VerificationTimeout=5s; VerificationRetryInterval=0.5s
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1281 TRACE - Set: Culture=en-US
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1285 TRACE - Set: Artifacts=D:\dev\AtataDemo.UITests\AtataDemo.UITests\bin\Debug\net7.0\artifacts\20231019T121624\SignInTests\SignIn
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1293 TRACE - > Initialize Driver
2023-10-19 12:16:24.1331 TRACE - - Created ChromeDriverService { Port=56112, ExecutablePath=D:\dev\AtataDemo.UITests\AtataDemo.UITests\bin\Debug\net7.0\drivers\chrome\118.0.5993.70\chromedriver.exe }
2023-10-19 12:16:24.8457 TRACE - - Created ChromeDriver { Alias=chrome, SessionId=40696ddb9dbb756cbcfb0de8ab0e8412 }
2023-10-19 12:16:24.8521 TRACE - < Initialize Driver (0.718s)
2023-10-19 12:16:24.8531 TRACE < Initialize AtataContext (0.728s)
2023-10-19 12:16:24.9119 INFO > Go to "Sign In" page by URL https://demo.atata.io/signin
2023-10-19 12:16:24.9130 TRACE - > Navigate to URL https://demo.atata.io/signin
2023-10-19 12:16:25.3187 TRACE - < Navigate to URL https://demo.atata.io/signin (0.405s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.3566 INFO < Go to "Sign In" page by URL https://demo.atata.io/signin (0.444s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.3692 INFO > Type "admin@mail.com" in "Email" text input
2023-10-19 12:16:25.3727 TRACE - > Execute behavior TypesTextUsingSendKeysAttribute against "Email" text input
2023-10-19 12:16:25.3960 TRACE - - > Find element by XPath "(.//*[@id = //label[normalize-space(.) = 'Email']/@for]/descendant-or-self::input[@type='text' or not(@type)] | .//label[normalize-space(.) = 'Email']/descendant-or-self::input[@type='text' or not(@type)])" in ChromeDriver
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4187 TRACE - - < Find element by XPath "(.//*[@id = //label[normalize-space(.) = 'Email']/@for]/descendant-or-self::input[@type='text' or not(@type)] | .//label[normalize-space(.) = 'Email']/descendant-or-self::input[@type='text' or not(@type)])" in ChromeDriver (0.021s) >> Element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_5 }
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4200 TRACE - - > Send keys "admin@mail.com" to element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_5 }
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4948 TRACE - - < Send keys "admin@mail.com" to element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_5 } (0.074s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4953 TRACE - < Execute behavior TypesTextUsingSendKeysAttribute against "Email" text input (0.122s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4954 INFO < Type "admin@mail.com" in "Email" text input (0.126s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4956 INFO > Type "abc123" in "Password" password input
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4959 TRACE - > Execute behavior TypesTextUsingSendKeysAttribute against "Password" password input
2023-10-19 12:16:25.4967 TRACE - - > Find element by XPath "(.//*[@id = //label[normalize-space(.) = 'Password']/@for]/descendant-or-self::input[@type='password'] | .//label[normalize-space(.) = 'Password']/descendant-or-self::input[@type='password'])" in ChromeDriver
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5115 TRACE - - < Find element by XPath "(.//*[@id = //label[normalize-space(.) = 'Password']/@for]/descendant-or-self::input[@type='password'] | .//label[normalize-space(.) = 'Password']/descendant-or-self::input[@type='password'])" in ChromeDriver (0.014s) >> Element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_6 }
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5120 TRACE - - > Send keys "abc123" to element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_6 }
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5612 TRACE - - < Send keys "abc123" to element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_6 } (0.049s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5620 TRACE - < Execute behavior TypesTextUsingSendKeysAttribute against "Password" password input (0.066s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5623 INFO < Type "abc123" in "Password" password input (0.066s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5628 INFO > Click "Sign In" button
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5637 TRACE - > Execute behavior ClicksUsingClickMethodAttribute against "Sign In" button
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5650 TRACE - - > Find element by XPath ".//*[self::input[@type='button' or @type='submit' or @type='reset'] or self::button][normalize-space(.) = 'Sign In' or normalize-space(@value) = 'Sign In']" in ChromeDriver
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5823 TRACE - - < Find element by XPath ".//*[self::input[@type='button' or @type='submit' or @type='reset'] or self::button][normalize-space(.) = 'Sign In' or normalize-space(@value) = 'Sign In']" in ChromeDriver (0.017s) >> Element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_10 }
2023-10-19 12:16:25.5830 TRACE - - > Click element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_10 }
2023-10-19 12:16:25.6589 TRACE - - < Click element { Id=899920EE3DDF8CF5FDC58EB63A55E6A0_element_10 } (0.075s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.6596 TRACE - < Execute behavior ClicksUsingClickMethodAttribute against "Sign In" button (0.095s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.6601 INFO < Click "Sign In" button (0.097s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.6614 TRACE > Deinitialize AtataContext
2023-10-19 12:16:25.8006 TRACE < Deinitialize AtataContext (0.139s)
2023-10-19 12:16:25.8046 INFO Finished test
Total time: 1.754s
Initialization: 0.806s | 46.0 %
Test body: 0.807s | 46.1 %
Deinitialization: 0.139s | 8.0 %
Demo
Demo atata-framework/atata-sample-app-tests UI tests application demonstrates different testing approaches and features of Atata Framework. It uses Atata Sample App (repository) as a testing website and NUnit 3 as a test engine.
Features
- Atata configuration and settings set-up.
- Page navigation.
- Controls finding.
- Data input and verification.
- Validation messages verification.
- Usage of triggers.
- Interaction with pop-ups (Bootstrap modal) and alerts.
- Work with tables.
- Logging, screenshots and snapshots.
- Page HTML validation.
Sample Test
public class UserTests : UITestFixture
{
[Test]
public void Create() =>
Login()
.New()
.ModalTitle.Should.Be("New User")
.General.FirstName.SetRandom(out string firstName)
.General.LastName.SetRandom(out string lastName)
.General.Email.SetRandom(out string email)
.General.Office.SetRandom(out Office office)
.General.Gender.SetRandom(out Gender gender)
.Save()
.GetUserRow(email).View()
.AggregateAssert(x => x
.Header.Should.Be($"{firstName} {lastName}")
.Email.Should.Be(email)
.Office.Should.Be(office)
.Gender.Should.Be(gender)
.Birthday.Should.Not.BeVisible()
.Notes.Should.Not.BeVisible());
//...
}
Configuration
In SetUp method just invoke AtataContext.Configure() method that returns AtataContextBuilder instance,
then invoke configuration methods and finally invoke Build() method:
[SetUp]
public void SetUp()
{
AtataContext.Configure()
// TODO: Use configuration methods.
.Build();
}
To clean up the AtataContext, call its Dispose method in the TearDown method:
[TearDown]
public void TearDown()
{
AtataContext.Current?.Dispose();
}
The Dispose method also, by default, closes a web driver instance as well as a browser.
Also, it is recommended to extract a global setup/configuration to the global setup method:
[SetUpFixture]
public class SetUpFixture
{
[OneTimeSetUp]
public void GlobalSetUp()
{
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
// TODO: Use configuration methods.
.AutoSetUpDriverToUse();
}
}
Consider taking a look at Atata.Configuration.Json for configuration through JSON files.
Driver
The list of driver configuration methods of AtataContextBuilder:
UseChrome()
Creates and returns a new builder for ChromeDriver
with default DriverAliases.Chrome alias.
Sets this builder as a one to use for a driver creation.
UseFirefox()
Creates and returns a new builder for FirefoxDriver
with default DriverAliases.Firefox alias.
Sets this builder as a one to use for a driver creation.
UseInternetExplorer()
Creates and returns a new builder for InternetExplorerDriver
with default DriverAliases.InternetExplorer alias.
Sets this builder as a one to use for a driver creation.
UseEdge()
Creates and returns a new builder for EdgeDriver
with default DriverAliases.Edge alias.
Sets this builder as a one to use for a driver creation.
UseSafari()
Creates and returns a new builder for SafariDriver
with default DriverAliases.Safari alias.
Sets this builder as a one to use for a driver creation.
UseRemoteDriver()
Creates and returns a new builder for RemoteWebDriver
with default DriverAliases.Remote alias.
Sets this builder as a one to use for a driver creation.
UseDriver(IWebDriver driver)
Use the specified driver instance.
UseDriver(Func<IWebDriver> driverFactory)
Use the custom driver factory method.
UseDriver
Use the driver builder.
UseDriver(string alias)
Sets the alias of the driver to use.
ConfigureChrome(string alias = DriverAliases.Chrome)
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for ChromeDriver by the specified alias.
ConfigureFirefox(string alias = DriverAliases.Firefox)
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for FirefoxDriver by the specified alias.
ConfigureInternetExplorer(string alias = DriverAliases.InternetExplorer)
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for InternetExplorerDriver by the specified alias.
ConfigureEdge(string alias = DriverAliases.Edge)
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for EdgeDriver by the specified alias.
ConfigureSafari(string alias = DriverAliases.Safari)
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for SafariDriver by the specified alias.
ConfigureRemoteDriver(string alias = DriverAliases.Remote)
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for RemoteWebDriver by the specified alias.
ConfigureDriver
Returns an existing or creates a new builder for TDriverBuilder by the specified alias.
UseDisposeDriver(bool disposeDriver)
Sets a value indicating whether to dispose the AtataContext.Driver when AtataContext.Dispose method is invoked.
The default value is true.
UseDriverInitializationStage(AtataContextDriverInitializationStage stage)
Sets the driver initialization stage.
The default value is AtataContextDriverInitializationStage.Build.
AutoSetUpDriverToUse()
AutoSetUpDriverToUseAsync()
Sets up driver with auto version detection for the local browser to use.
Gets the name of the local browser to use from AtataBuildingContext.LocalBrowserToUseName property.
Then invokes Atata.WebDriverSetup.DriverSetup.AutoSetUpSafely(...) static method
from Atata.WebDriverSetup package.
AutoSetUpConfiguredDrivers()
AutoSetUpConfiguredDriversAsync()
Sets up drivers with auto version detection for the local configured browsers.
Gets the names of configured local browsers from AtataBuildingContext.ConfiguredLocalBrowserNames property.
Then invokes Atata.WebDriverSetup.DriverSetup.AutoSetUpSafely(...) static method
from Atata.WebDriverSetup package.
Driver Configuration
It is possible to configure the driver using the following methods of driver builders. The amount of methods vary dependently of the driver builder type, for example Chrome and Edge builders support the most amount.
WithArguments(params string[] arguments)
WithArguments(IEnumerable<string> arguments)
Adds arguments to be appended to the browser executable command line.
WithAlias(string alias)
Specifies the driver alias.
WithDownloadDirectory(string directoryPath)
Adds the download.default_directory user profile preference to options
with the value specified by directoryPath.
WithDownloadDirectory(Func<string> directoryPathBuilder)
Adds the download.default_directory user profile preference to options
with the value specified by directoryPathBuilder.
WithArtifactsAsDownloadDirectory()
Adds the download.default_directory user profile preference to options
with the value of Artifacts directory path.
WithOptions{DriverOptions} options)
Specifies the driver options.
WithOptions(Func<{DriverOptions}> optionsCreator)
Specifies the driver options factory method.
WithOptions(Action<{DriverOptions}> optionsInitializer)
Specifies the driver options initialization method.
WithOptions(Dictionary
Specifies the properties map for the driver options.
AddAdditionalOption(string optionName, object optionValue)
Adds the additional option to the driver options.
AddAdditionalBrowserOption(string optionName, object optionValue)
Adds the additional browser option to the driver options.
WithDriverService(Func<{DriverService}> driverServiceCreator)
Specifies the driver service factory method.
WithDriverService(Action
Specifies the driver service initialization method.
WithDriverService(Dictionary
Specifies the properties map for the driver service.
WithDriverPath(string driverPath)
Specifies the directory containing the driver executable file.
WithLocalDriverPath()
Specifies that local/current directory should be used as the directory containing the driver executable file.
Uses AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory as driver folder path.
This configuration option makes sense for .NET Core 2.0+ project that uses driver as a project package (hosted in the same build directory).
WithDriverExecutableFileName(string driverExecutableFileName)
Specifies the name of the driver executable file.
WithCommandTimeout(TimeSpan commandTimeout)
Specifies the command timeout (the maximum amount of time to wait for each command). The default timeout is 60 seconds.
WithHostName(string hostName)
Specifies the host name of the service.
The default value is localhost.
Can be set to "127.0.0.1", for example when you experience localhost resolve issues.
WithCreateRetries(int createRetries)
Specifies the count of possible driver creation retries in case exceptions occur during creation.
The default value is 2.
Set 0 to omit retries.
WithInitialHealthCheck(bool enable = true)
Enables or disables an initial health check.
By default it is disabled.
When enabled, the default health check function requests IWebDriver.Url.
The health check function can be changed by using WithInitialHealthCheckFunction(Func<IWebDriver, bool>) method.
WithInitialHealthCheckFunction(Func<IWebDriver, bool> function)
Sets the initial health check function.
The default function requests IWebDriver.Url.
WithPortsToIgnore(params int[] portsToIgnore)
WithPortsToIgnore(IEnumerable<int> portsToIgnore)
Specifies the ports to ignore.
Usage
An example of using headless Chrome.
AtataContext.Configure()
.UseChrome()
.WithArguments("headless=new", "window-size=1200,800")
.Build();
Logging
Atata generates many log entries during execution and send them to log consumers.
The log consumers can be registered through the methods of LogConsumers property of AtataContextBuilder.
The list of log consumers methods of LogConsumersAtataContextBuilder:
Add
where TLogConsumer : ILogConsumer, new()
Adds the log consumer.
Add
where TLogConsumer : ILogConsumer
Adds the log consumer.
Add(string typeNameOrAlias)
Adds the log consumer by its type name or alias.
Predefined aliases are defined in LogConsumerAliases static class.
Configure
where TLogConsumer : ILogConsumer, new()
Returns a log consumer builder for existing TLogConsumer log consumer or adds a new one.
AddTrace()
Adds the TraceLogConsumer instance that uses System.Diagnostics.Trace class for logging.
AddDebug()
Adds the DebugLogConsumer instance that uses System.Diagnostics.Debug class for logging.
AddConsole()
Adds the ConsoleLogConsumer instance that uses System.Console class for logging.
AddNUnitTestContext()
Adds the NUnitTestContextLogConsumer instance that uses NUnit.Framework.TestContext class for logging.
AddNLog(string loggerName = null)
Adds the NLogConsumer instance that uses NLog.Logger class for logging.
AddNLogFile()
Adds the NLogFileConsumer instance that uses NLog.Logger class for logging into file.
AddLog4Net(string loggerName = null)
Adds the Log4NetConsumer instance that uses log4net.ILog interface for logging.
AddLog4Net(string repositoryName, string loggerName = null)
Adds the Log4NetConsumer instance that uses log4net.ILog interface for logging.
AddLog4Net(Assembly repositoryAssembly, string loggerName = null)
Adds the Log4NetConsumer instance that uses log4net.ILog interface for logging.
Logging Configuration
The list of LogConsumerAtataContextBuilder<TLogConsumer> methods to configure ILogConsumer:
WithSectionEnd(LogSectionEndOption logSectionEnd)
Sets the output option of log section end.
The default value is LogSectionEndOption.Include.
Other options are: LogSectionEndOption.IncludeForBlocks and LogSectionEndOption.Exclude.
If section end is excluded, instead of “Starting: {action}” and “Finished: {action} {time elapsed}”, just “{action}” is outputted.
WithMinLevel(LogLevel level)
Specifies the minimum level of the log event to write to the log. The default value is Trace.
WithMessageNestingLevelIndent(string messageNestingLevelIndent)
Sets the nesting level indent of the log message.
The default value is "- ".
WithMessageStartSectionPrefix(string messageStartSectionPrefix)
Sets the start section prefix of the log message.
The default value is "> ".
WithMessageEndSectionPrefix(string messageEndSectionPrefix)
Sets the end section prefix of the log message.
The default value is "< ".
Usage
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.LogConsumers.AddNLogFile()
.LogConsumers.AddNUnitTestContext()
.WithSectionEnd(LogSectionEndOption.Exclude)
.WithMinLevel(LogLevel.Info);
Screenshots
The screenshots functionality can be configured through the methods of Screenshots property of AtataContextBuilder.
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.Screenshots.UseFullPageOrViewportStrategy()
.Screenshots.UseFileNameTemplate("{screenshot-number:D2}...");
Screenshot strategy is a way how a screenshot should be taken, basically it can either a viewport area or a full-page screenshot. By default, the viewport taking strategy is used.
The list of ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder methods:
UseWebDriverViewportStrategy()
Sets the WebDriver viewport (WebDriverViewportScreenshotStrategy) strategy for a screenshot taking.
UseWebDriverFullPageStrategy()
Sets the WebDriver full-page (WebDriverFullPageScreenshotStrategy) strategy for a screenshot taking.
Works only for FirefoxDriver.
UseCdpFullPageStrategy()
Sets the CDP full-page (CdpFullPageScreenshotStrategy) strategy for a screenshot taking.
Works only for ChromeDriver and EdgeDriver.
UseFullPageOrViewportStrategy()
Sets the “full-page or viewport” (FullPageOrViewportScreenshotStrategy) strategy for a screenshot taking.
UseStrategy(IScreenshotStrategy strategy)
Sets the strategy for a screenshot taking.
The default value is an instance of WebDriverViewportScreenshotStrategy.
UseFileNameTemplate(string fileNameTemplate)
Sets the file name template of page screenshots.
The default value is "{screenshot-number:D2}{screenshot-pageobjectname: *}{screenshot-pageobjecttypename: *}{screenshot-title: - *}".
Page Snapshots
The page snapshot functionality can be configured through the methods of PageSnapshots property of AtataContextBuilder.
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.PageSnapshots.UseCdpStrategy()
.PageSnapshots.UseFileNameTemplate("{snapshot-number:D2}...");
The default strategy is CdpOrPageSourcePageSnapshotStrategy.
The list of PageSnapshotsAtataContextBuilder methods:
UseCdpOrPageSourceStrategy()
Sets the “CDP or page source” (CdpOrPageSourcePageSnapshotStrategy) strategy for a page snapshot taking.
UsePageSourceStrategy()
Sets the page source (PageSourcePageSnapshotStrategy) strategy for a page snapshot taking.
UseCdpStrategy()
Sets the CDP (CdpPageSnapshotStrategy) strategy for a page snapshot taking.
UseStrategy(IPageSnapshotStrategy strategy)
Sets the strategy for a page snapshot taking.
The default value is an instance of CdpOrPageSourcePageSnapshotStrategy.
UseFileNameTemplate(string fileNameTemplate)
Sets the file name template of page snapshots.
The default value is "{snapshot-number:D2}{snapshot-pageobjectname: *}{snapshot-pageobjecttypename: *}{snapshot-title: - *}".
Event Subscriptions
Atata provides a set of events that are raised during execution.
Event handlers can be subscribed on Atata or custom events through the methods of EventSubscriptions property of AtataContextBuilder.
The list of Atata events:
AtataContextPreInitEventAtataContextInitStartedEventAtataContextInitCompletedEventAtataContextDeInitEventAtataContextDeInitCompletedEventDriverInitEventDriverDeInitEventPageObjectInitEventPageObjectInitCompletedEventPageObjectDeInitEventArtifactAddedEvent
The list of methods of EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder:
Add<TEvent>
Add<TEvent>
Add<TEvent>
Add<TEvent>
Adds the specified event handler as a subscription to the TEvent.
Add<TEvent, TEventHandler>
where TEventHandler : class, IEventHandler<TEvent>, new()
Adds the created instance of TEventHandler as a subscription to the TEvent.
Add<TEvent>
Adds the created instance of eventHandlerType as a subscription to the eventType.
Add<TEvent>
Adds the created instance of eventHandlerType as a subscription to the event type
that is read from IEventHandler<TEvent> generic argument that eventHandlerType should implement.
Usage
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.EventSubscriptions.Add<DriverInitEvent>(e => e.Driver.Maximize());
NUnit Event Handlers
LogNUnitError()
Defines that an error occurred during the NUnit test execution should be added to the log during AtataContext deinitialization.
TakeScreenshotOnNUnitError(string title = "Failed")
TakeScreenshotOnNUnitError(ScreenshotKind kind, string title = "Failed")
Defines that an error occurred during the NUnit test execution should be captured by a screenshot during AtataContext deinitialization.
TakePageSnapshotOnNUnitError(string title = "Failed")
Defines that an error occurred during the NUnit test execution should be captured by a page snapshot during AtataContext deinitialization.
AddArtifactsToNUnitTestContext()
Defines that after AtataContext deinitialization the files stored in Artifacts directory
should be added to NUnit TestContext.
AddDirectoryFilesToNUnitTestContext(string directoryPath)
AddDirectoryFilesToNUnitTestContext(Func<string> directoryPathBuilder)
AddDirectoryFilesToNUnitTestContext(Func<AtataContext, string> directoryPathBuilder)
Defines that after AtataContext deinitialization the files stored in the
specified directory should be added to NUnit TestContext.
Directory path supports template variables.
Global Properties
The static AtataContext.GlobalProperties property
contains global properties that should be configured as early as possible,
typically in global setup method before any creation of AtataContext, and not changed later,
because these properties should have the same values for all the contexts within an execution.
AtataContext.GlobalProperties
.UseUtcTimeZone()
.UseArtifactsRootPathTemplate("{basedir}/artifacts");
The list of AtataContextGlobalProperties configuration methods:
UseArtifactsRootPathTemplate(string directoryPathTemplate)
Sets the path template of the Artifacts Root directory.
The default value is "{basedir}/artifacts/{build-start:yyyyMMddTHHmmss}".
The list of supported variables:
{basedir}{build-start}{build-start-utc}
UseDefaultArtifactsRootPathTemplateIncludingBuildStart(string include)
Sets the default Artifacts Root path template with optionally
including "{build-start:yyyyMMddTHHmmss}" folder in the path.
UseTimeZone(TimeZoneInfo timeZone)
Sets the time zone.
UseTimeZone(string timeZoneId)
Sets the time zone by identifier, which corresponds to the TimeZoneInfo.Id property.
UseUtcTimeZone()
Sets the UTC time zone.
UseModeOfCurrent(AtataContextModeOfCurrent mode)
Sets the mode of AtataContext.Current property.
The default value is AtataContextModeOfCurrent.AsyncLocal.
Other
UseBaseUrl(string baseUrl)
Sets the base URL.
UseCulture(CultureInfo culture)
Sets the culture. The default value is CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.
UseCulture(string cultureName)
Sets the culture by the name. The default value is CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.
UseArtifactsPathTemplate(string directoryPathTemplate)
Sets the Artifacts directory path template.
The default value is "{test-suite-name-sanitized:/*}{test-name-sanitized:/*}".
The list of predefined variables:
{test-name-sanitized}{test-name}{test-suite-name-sanitized}{test-suite-name}{test-start}{test-start-utc}{driver-alias}
UseAllNUnitFeatures()
Enables all Atata features for NUnit. Executes the following methods:
UseNUnitTestName()UseNUnitTestSuiteName()UseNUnitTestSuiteType()UseNUnitAssertionExceptionType()UseNUnitAggregateAssertionStrategy()UseNUnitWarningReportStrategy()UseNUnitAssertionFailureReportStrategy()LogConsumers.AddNUnitTestContext()EventSubscriptions.LogNUnitError()EventSubscriptions.TakeScreenshotOnNUnitError()EventSubscriptions.TakePageSnapshotOnNUnitError()EventSubscriptions.AddArtifactsToNUnitTestContext()
UseSpecFlowNUnitFeatures()
Enables all Atata features for SpecFlow+NUnit. Executes the following methods:
UseNUnitTestName()UseNUnitTestSuiteName()UseNUnitTestSuiteType()UseNUnitAssertionExceptionType()UseNUnitAggregateAssertionStrategy()UseNUnitWarningReportStrategy()UseNUnitAssertionFailureReportStrategy()EventSubscriptions.LogNUnitError()EventSubscriptions.TakeScreenshotOnNUnitError()EventSubscriptions.TakePageSnapshotOnNUnitError()
UseTestName(string testName)
Sets the name of the test.
UseTestName(Func
Sets the factory method of the test name.
UseNUnitTestName()
Defines that the name of the test should be taken from the NUnit test.
UseTestSuiteName(string testSuiteName)
Sets the name of the test suite (fixture/class).
UseTestSuiteName(Func
Sets the factory method of the test suite (fixture/class) name.
UseNUnitTestSuiteName()
Defines that the name of the test suite should be taken from the NUnit test fixture.
UseTestSuiteType(Type testSuiteType)
Sets the type of the test suite (fixture/class).
UseTestSuiteType(Func
Sets the factory method of the test suite (fixture/class) type.
UseNUnitTestSuiteType()
Defines that the type of the test suite should be taken from the NUnit test fixture.
UseBaseRetryTimeout(TimeSpan timeout)
Sets the base retry timeout. The default value is 5 seconds
UseBaseRetryInterval(TimeSpan interval)
Sets the base retry interval. The default value is 500 milliseconds.
UseElementFindTimeout(TimeSpan timeout)
Sets the element find timeout.
The default value is taken from AtataBuildingContext.BaseRetryTimeout, which is equal to 5 seconds by default.
UseElementFindRetryInterval(TimeSpan interval)
Sets the element find retry interval.
The default value is taken from AtataBuildingContext.BaseRetryInterval, which is equal to 500 milliseconds by default.
UseWaitingTimeout(TimeSpan timeout)
Sets the waiting timeout.
The default value is taken from AtataBuildingContext.BaseRetryTimeout, which is equal to 5 seconds by default.
UseWaitingRetryInterval(TimeSpan interval)
Sets the waiting retry interval.
The default value is taken from AtataBuildingContext.BaseRetryInterval, which is equal to 500 milliseconds by default.
UseVerificationTimeout(TimeSpan timeout)
Sets the verification timeout.
The default value is taken from AtataBuildingContext.BaseRetryTimeout, which is equal to 5 seconds by default.
UseVerificationRetryInterval(TimeSpan interval)
Sets the verification retry interval.
The default value is taken from AtataBuildingContext.BaseRetryInterval, which is equal to 500 milliseconds by default.
UseAssertionExceptionType(Type exceptionType)
Sets the type of the assertion exception. The default value is typeof(Atata.AssertionException).
UseAssertionExceptionType
Sets the type of the assertion exception. The default value is typeof(Atata.AssertionException).
AddVariable(string key, object value)
Adds the variable.
AddVariables(IDictionary<string, object> variables)
Adds the variables.
AddSecretStringToMaskInLog(string value, string mask = "{*****}")
Adds the secret string to mask in log.
UseDomTestIdAttributeName(string name)
Sets the name of the DOM test identifier attribute.
The default value is "data-testid".
UseDomTestIdAttributeDefaultCase(TermCase defaultCase)
Sets the default case of the DOM test identifier attribute.
The default value is TermCase.Kebab.
Clear()
Clears the BuildingContext.
Build()
Builds the AtataContext instance and sets it to AtataContext.Current property.
Navigation
Go
A page object navigation starts with Go static class, or alternatively with Go property of AtataContext instance.
Both Go approaches provide a set of similar methods for navigation.
Methods
To<T>(T pageObject = null, string url = null, bool navigate = true, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to the specified page object.
On<T>()
where T : PageObject<T>Continues with the specified page object type.
Firstly, checks whether the current AtataContext.PageObject
is T, if it is, returns it;
otherwise, creates a new instance of T without navigation.
The method is useful in case when in a particular step method (BDD step, for example)
you don’t have an instance of current page object but you are sure that a browser is on the needed page.
OnRefreshed<T>()
where T : PageObject<T>Continues with the specified page object type with rage refresh.
Firstly, checks whether the current AtataContext.PageObject
is T, if it is, returns it;
otherwise, creates a new instance of T without navigation.
Then a page is refreshed.
The method is useful in case when you reuse a single test suite driver by tests and
want to refresh a page on start of each test to ensure that the page is in clean start state.
OnOrTo<T>()
where T : PageObject<T>Continues with the specified page object type or navigates to it.
Firstly, checks whether the current AtataContext.PageObject
is T, if it is, returns it; otherwise, creates a new instance of T with navigation.
The method is useful in case when in a particular step method (BDD step, for example)
you don’t have an instance of current page object and you are not sure that a browser is on the needed page, but can be.
ToWindow<T>(T pageObject, string windowName, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to the window with the specified page object by name.
ToWindow<T>(string windowName, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to the window by name.
ToNextWindow<T>(T pageObject = null, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to the next window with the specified page object.
ToPreviousWindow<T>(T pageObject = null, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to the previous window with the specified page object.
ToUrl(string url)
Navigates to the specified URL.
ToNewWindow<T>(T pageObject = null, string url = null, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to a new window with the specified page object.
ToNewWindowAsTab<T>(T pageObject = null, string url = null, bool temporarily = false)
where T : PageObject<T>Navigates to a new tab window with the specified page object.
Usage
Go.To<HomePage>()
.Header.Should.Equal("Home");
Go.To<AboutPage>(url: "/about")
.Should.Equal("About");
By Static URL
Every page object can have a static URL associated with it by UrlAttribute.
This URL is consumed during Go.To action to perform a navigation.
The URL can be an absolute, but it’s recommended to use a relative URL,
it will be concatenated with BaseUrl to form an absolute URL.
Example
[Url("/contact")]
public class ContactPage : Page<_>
{
}
Go.To<ContactPage>();
By Dynamic URL
When a page object’s URL is dynamic (contains identifiers in path, query parameters, etc.), one of the following approaches can be used for assigning a dynamic URL to a page object.
Pass URL in Go.To Method
Go.To<UserPage>(url: $"/user/{userId}");
Set NavigationUrl
PageObject<TOwner> has the NavigationUrl property which can be assigned in a page object’s constructor.
Static URL (a value of UrlAttribute) is also written to NavigationUrl in a base constructor,
so you can combine static URL part with dynamic part.
Example 1
public class UserPage : Page<_>
{
public UserPage(int? id = null)
{
if (id.HasValue)
NavigationUrl = $"/user/{id}";
}
}
Go.To(new UserPage(42));
Example 2
public class UserPage : Page<_>
{
// Default constructor is needed for non-direct navigation, for example via link click.
public UserPage()
{
}
public UserPage(int id)
{
NavigationUrl = $"/user/{id}";
}
}
Go.To(new UserPage(42));
Example 3
public class UserPage : Page<_>
{
public static _ ById(int id) =>
new() { NavigationUrl = $"/user/{id}" };
}
Go.To(UserPage.ById(42));
Example 4
Static URL can be combined with dynamic part.
[Url("/search")]
public class GoogleSearchPage : Page<_>
{
public GoogleSearchPage(string query = null)
{
if (query != null)
NavigationUrl += $"?q={query}"; // "/search" + $"?q={query}" = "/search?q={query}"
}
}
Go.To<GoogleSearchPage>();
// Or:
Go.To(new GoogleSearchPage("keyword"));
Example 5
Similar to the previous example, but uses static method instead of constructor.
[Url("/search")]
public class GoogleSearchPage : Page<_>
{
public static _ WithQuery(string query) =>
new _().AppendNavigationUrl($"?q={query}");
}
Go.To<GoogleSearchPage>();
// Or:
Go.To(GoogleSearchPage.WithQuery("keyword"));
By Combined URL
Go.To method’s url argument value combines with page object’s NavigationUrl
if it starts with one of: ?, &, ;, #.
For other cases url argument value replaces the NavigationUrl.
Basically, you can combine static URL part with dynamic one.
Example
[Url("/some/path?a=1")]
public class SomePage : Page<_>
{
}
Go.To<SomePage>(url: "/another/path?b=2"); // -> "/another/path?b=2"
Go.To<SomePage>(url: "?b=2"); // -> "/some/path?b=2"
Go.To<SomePage>(url: "&b=2"); // -> "/some/path?a=1&b=2"
Go.To<SomePage>(url: ";b=2"); // -> "/some/path?a=1;b=2"
Go.To<SomePage>(url: "#fragment"); // -> "/some/path?a=1#fragment"
URL Template Variables
Template variables are allowed in UrlAttribute and Go.To method’s url parameter.
The URL can be represented in a template format, like "/organization/{OrganizationId}/".
The template is filled with AtataContext.Variables by using AtataContext.FillUriTemplateString(string)
method (see #738).
In order to output a { use {{, and to output a } use }}.
Before navigation ensure that a variable is set in AtataContext.
Set variable directly into AtataContext
AtataContext.Current.Variables["OrganizationId"] = 42;
Set variable during AtataContext configuration
AtataContext.Configure().
AddVariable("OrganizationId", 42);
Set variable in JSON config
{
"variables": {
"OrganizationId": 42
}
}
Use template in UrlAttribute
[Url("/organization/{OrganizationId}/")]
public class OrganizationPage : Page<_>
{
}
Go.To<OrganizationPage>();
Use template within Go.To
Go.To<OrganizationPage>(url: "/organization/{OrganizationId}/");
Transition
A transition from one page object to another is implemented via controls:
Button, Link and Clickable.
Also a transition can be specified via adding INavigable<,> interface to a custom control.
Example
For example, having 3 simple pages on a site:
- “Users” page with users table and “New” link that navigates to the “User Editor” page. Clicking on a user row redirects to the “User Details” page.
- “User Editor” page that contains “Name” input field and “Save” button that redirect back to “Users” page.
- “User Details” page containing the name of the user.
UsersPage.cs
using Atata;
namespace SampleApp.UITests;
using _ = UsersPage;
[Url("users")]
public class UsersPage : Page<_>
{
public Link<UserEditorPage, _> New { get; private set; }
public Table<UserTableRow, _> Users { get; private set; }
public class UserTableRow : TableRow<_>, INavigable<UserDetailsPage, _>
{
public Text<_> Name { get; private set; }
}
}
UserEditorPage.cs
using Atata;
namespace SampleApp.UITests;
using _ = UserEditorPage;
public class UserEditorPage : Page<_>
{
public TextInput<_> Name { get; private set; }
public Button<UsersPage, _> Save { get; private set; }
}
UserDetailsPage.cs
using Atata;
namespace SampleApp.UITests;
using _ = UserDetailsPage;
public class UserDetailsPage : Page<_>
{
public H1<_> Name { get; private set; }
}
Usage
string userName;
Go.To<UsersPage>()
.New.ClickAndGo() // Navigates to UserEditorPage.
.Name.SetRandom(out userName) // Sets the random value to Name field and stores it to userName variable.
.Save.ClickAndGo() // Clicking the Save button navigates back to UsersPage.
.Users.Rows[x => x.Name == userName].ClickAndGo() // Clicking the row navigates to UserDetailsPage.
.Name.Should.Equal(userName);
Reporting
Reporting in Atata Framework consists of logging and artifact files.
The testing artifacts can be: log files, screenshots, page snapshots, downloaded files, etc.
All artifact files can be placed to the AtataContext.Artifacts directory.
By default, as it is recommended to be, AtataContext.Artifacts directory is unique per test.
The default Artifacts path follows the template:
{working_directory}\artifacts\{tests_run_timestamp}\{test_suite_name}\{test_name}"
For example:
{project_directory}\bin\Debug\net7.0\artifacts\20231014T112506\SomeTests\Test1
Atata by itself writes a lot of log entries during execution, but custom log entries and artifact files can be reported as well.
There is also Reporting to ExtentReports tutorial, which describes how to configure Atata reporting to ExtentReports.
Report<TOwner> class
The main class for reporting is Report<TOwner>.
An instance of Report<TOwner> can be got by Report property of either AtataContext or PageObject<TOwner>.
AtataContext.Current.Report.Info("Hello world!");
Go.To<SomePage>()
.Report.Step("Doing some step", x => x
.SomeInput.Type("some text")
.SomeButton.Click())
.Report.Screenshot();
Methods
Trace(string message)
Writes a trace log message.
Debug(string message)
Writes a debug log message.
Info(string message)
Writes an informational log message.
Warn(Exception exception)
Warn(string message)
Warn(Exception exception, string message)
Writes a warning log message.
Error(Exception exception)
Error(string message)
Error(Exception exception, string message)
Writes an error log message.
Fatal(Exception exception)
Fatal(string message)
Fatal(Exception exception, string message)
Writes a critical log message.
Setup(string message, Action<TOwner> action)
Setup<TResult>(string message, Func<TOwner, TResult> function)
Executes the specified action/function and represents it in a log as a setup section with the specified message. The setup action time is not counted as a “Test body” execution time, but counted as “Setup” time.
Setup<TPageObject>(Func<TOwner, TPageObject> function)
Executes the specified function and represents it in a log as a setup section with the message like "Set up "<Some>" page".
The setup function time is not counted as a “Test body” execution time, but counted as “Setup” time.
Step(string message, Action<TOwner> action)
Step<TResult>(string message, Func<TOwner, TResult> function)
Executes the specified action/function and represents it in a log as a section with the specified message.
Screenshot(string title = null)
Takes a screenshot of the current page with an optionally specified title.
Screenshot(ScreenshotKind kind, string title = null)
Takes a screenshot of the current page of a certain kind with an optionally specified title.
PageSnapshot(string title = null)
Takes a snapshot (HTML or MHTML file) of the current page with an optionally specified title.
Screenshots Taking
Take a look at Getting Started / Configuration / Screenshots on how to configure the functionality.
There are few ways to capture a screenshot depending on place where you need to do it.
Take in test or page object
Use Report.Screenshot(...) method:
Go.To<OrdinaryPage>()
.Report.Screenshot();
//.Report.Screenshot("optional title"); // To specify a title.
//.Report.Screenshot(ScreenshotKind.FullPage); // To specify a kind (FullPage/Viewport).
Take in any place
AtataContext.Current.TakeScreenshot();
AtataContext.Current.Report.Screenshot();
Take using trigger
Use TakeScreenshot trigger. Below are just 2 possible scenarios.
Before button click
[TakeScreenshot(TriggerEvents.BeforeClick)]
// [TakeScreenshot("optional title", TriggerEvents.BeforeClick)] // To specify a title.
// [TakeScreenshot(ScreenshotKind.FullPage, TriggerEvents.BeforeClick)] // To specify a kind.
public Button<_> Save { get; private set; }
Upon page object initialization
[TakeScreenshot(TriggerEvents.Init)]
public class SomePage : Page<_>
{
}
Full-page screenshots
There is a possibility to take full-page screenshots. The functionality is not enabled by default. Also, currently it works only for Chrome, Edge and Firefox, so enable it carefully.
Enable full-page screenshots by default
Full-page screenshots can be enabled to be taken by default instead of viewport screenshots.
Configuration
Use Screenshots property of AtataContextBuilder:
public ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder Screenshots { get; }
ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder contains the following methods:
// Used by default.
public ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder UseWebDriverViewportStrategy();
// Works only for Firefox.
public ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder UseWebDriverFullPageStrategy();
// Works only for Chrome and Edge.
public ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder UseCdpFullPageStrategy();
// *** Recommended to use for full-page screenshots, regardless of browser/driver.
public ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder UseFullPageOrViewportStrategy();
// To use custom strategy.
public ScreenshotsAtataContextBuilder UseStrategy(IScreenshotStrategy strategy);
Usage
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.Screenshots.UseFullPageOrViewportStrategy();
Explicitly take full-page screenshots
It is also possible to take full-page screenshots only at certain points.
It is allowed to explicitly specify ScreenshotKind enum value depending whether you need a viewport or a full-page screenshot.
ScreenshotKind enum provides 3 values: Default, Viewport and FullPage.
Examples
AtataContext.Current.TakeScreenshot(ScreenshotKind.FullPage);
Go.To<SomePage>()
.Report.Screenshot(ScreenshotKind.FullPage);
[TakeScreenshot(ScreenshotKind.FullPage, TriggerEvents.Init)]
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.TakeScreenshotOnNUnitError(ScreenshotKind.FullPage);
Page Snapshots Taking
A page snapshot can be either HTML or MHTML file.
For Chromium-based browsers (Chrome and Edge) a snapshot by default is taken using CDP command Page.captureSnapshot and saved as .MHTML file with styles and images.
Note that Page.captureSnapshot command is in experimental state
so the result page snapshot may not 100% be equal to an original page.
For other browsers a snapshot is taken using IWebDriver.PageSource property
and saved as .HTML file without styles.
Take a look at Getting Started / Configuration / Page Snapshots on how to configure the functionality.
There are few ways to capture a page snapshot depending on place where you need to do it.
Take in test or page object
Use Report.PageSnapshot(...) method:
Go.To<OrdinaryPage>()
.Report.PageSnapshot();
//.Report.PageSnapshot("optional title"); // To specify a title.
Take in any place
AtataContext.Current.TakePageSnapshot();
AtataContext.Current.Report.PageSnapshot();
Take using trigger
Use TakePageSnapshot trigger. Below are just 2 possible scenarios.
Before button click
[TakePageSnapshot(TriggerEvents.BeforeClick)]
// [TakePageSnapshot("optional title", TriggerEvents.BeforeClick)] // To specify a title.
public Button<_> Save { get; private set; }
Upon page object initialization
[TakePageSnapshot(TriggerEvents.Init)]
public class SomePage : Page<_>
{
}
Browser Logs Monitoring
Currently this functionality is available only for Chrome and Edge, both local and remote.
The feature brings a monitoring of browser logs, such as warnings and errors, which happen during a test execution. Browser logs can be transferred to Atata logs and can raise warnings.
In order to enable browser logs monitoring, configure AtataContext in the following way:
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.BrowserLogs.UseLog()
.BrowserLogs.UseMinLevelOfWarning(LogLevel.Warn);
Or in Atata JSON config:
{
"browserLogs": {
"log": true,
"minLevelOfWarning": "warn" // Supports: "trace", "debug", "info", "warn", "error", "fatal".
}
}
UseLog(bool enable = true) - sets a value indicating whether the browser log should be transferred to Atata logging system. The default value is false.
UseMinLevelOfWarning(LogLevel? minLevel) - sets the minimum log level on which to raise warnings. The default value is null, meaning that warning is disabled. For example, setting the LogLevel.Warn value will mean to warn on browser log entries with LogLevel.Warn level and higher, which are LogLevel.Error and LogLevel.Fatal.
A log entry in Atata log can look like:
2023-08-26 20:41:49.3187 TRACE - Browser log: 20:41:49.2800 ERROR http://localhost:54321/browserlogs 17:10 Uncaught Error: Some thrown error.
A warning looks this way:
Unexpected browser log error on "<ordinary>" page:
http://localhost:54321/browserlogs 17:10 Uncaught Error: Some thrown error.
JavaScript Popup Boxes
The fluent API for handling JavaScript popup boxes (alert, confirm, prompt).
The base PageObject<TOwner> class has 3 methods for different popup boxes:
public AlertBox<TOwner> SwitchToAlertBox(TimeSpan? waitTimeout = null, TimeSpan? waitRetryInterval = null);
public ConfirmBox<TOwner> SwitchToConfirmBox(TimeSpan? waitTimeout = null, TimeSpan? waitRetryInterval = null);
public PromptBox<TOwner> SwitchToPromptBox(TimeSpan? waitTimeout = null, TimeSpan? waitRetryInterval = null);
The methods wait and switch to the open popup box. By default, if waitTimeout and waitRetryInterval arguments are not specified, the AtataContext.WaitingTimeout and AtataContext.WaitingRetryInterval values are used correspondingly. If popup box does not appear within the specified time, the TimeoutException is thrown.
Alert
Go.To<SomePage>()
.AlertButton.Click()
.SwitchToAlertBox()
.Accept();
Confirm
Go.To<SomePage>()
.ConfirmButton.Click()
.SwitchToConfirmBox()
.Accept(); // or Cancel()
Prompt
Go.To<SomePage>()
.PromptButton.Click()
.SwitchToPromptBox()
.Type("Some text")
.Accept(); // or Cancel()
Verify Popup Text
Use Text property of popup box classes to get or verify the text of popup.
page.SwitchToAlertBox()
.Text.Should.Be("Some text");
Events
The events functionality allows to subscribe to Atata built-in and custom events as well as publish events.
EventBus
The core of the functionality is IEventBus interface,
which can used to subscribe to and publish events at any time of test cycle.
The IEventBus object is accessible through the EventBus property of AtataContext.
IEventBus provides the following methods:
void Publish<TEvent>(TEvent eventData);
object Subscribe<TEvent>(Action eventHandler);
object Subscribe<TEvent>(Action<TEvent> eventHandler);
object Subscribe<TEvent>(Action<TEvent, AtataContext> eventHandler);
object Subscribe<TEvent, TEventHandler>()
where TEventHandler : class, IEventHandler<TEvent>, new();
object Subscribe<TEvent>(IEventHandler<TEvent> eventHandler);
void Unsubscribe(object subscription);
void UnsubscribeHandler(object eventHandler);
void UnsubscribeAll<TEvent>();
void UnsubscribeAll(Type eventType);
IEventHandler
The event handler interface to implement for event handler classes:
public interface IEventHandler<in TEvent>
{
void Handle(TEvent eventData, AtataContext context);
}
IConditionalEventHandler
The event handler interface to implement for conditional event handler classes:
public interface IConditionalEventHandler<in TEvent> : IEventHandler<TEvent>
{
bool CanHandle(TEvent eventData, AtataContext context);
}
EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder
EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder - the builder of event subscriptions, which is available through EventSubscriptions property of AtataContextBuilder.
It provides the methods to subscribe to Atata and custom events during AtataContext building.
The list of its methods:
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add<TEvent>(Action eventHandler);
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add<TEvent>(Action<TEvent> eventHandler);
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add<TEvent>(Action<TEvent, AtataContext> eventHandler);
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add<TEvent, TEventHandler>()
where TEventHandler : class, IEventHandler<TEvent>, new();
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add<TEvent>(IEventHandler<TEvent> eventHandler);
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add(Type eventHandlerType);
public EventSubscriptionsAtataContextBuilder Add(Type eventType, Type eventHandlerType);
Usage
Subscribe Action Event Handler
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.EventSubscriptions.Add<DriverInitEvent>(e => e.Driver.Maximize());
Subscribe Action Event Handler as a Method
Method can have no parameters, single event type parameter, or event type parameter with AtataContext parameter.
Examples:
private static void OnDriverInit()
{
}
private static void OnDriverInit(DriverInitEvent eventData)
{
}
private static void OnDriverInit(DriverInitEvent eventData, AtataContext context)
{
}
Then subscribe it:
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.EventSubscriptions.Add<DriverInitEvent>(OnDriverInit);
Create and Subscribe Specific Event Handler Class
Create an event handler class, for example for DriverInitEvent:
public class DriverInitEventHandler : IEventHandler<DriverInitEvent>
{
public void Handle(DriverInitEvent eventData, AtataContext context)
{
// TODO: Implement.
}
}
Subscribe it during AtataContext building:
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.EventSubscriptions.Add(new DriverInitEventHandler());
Create and Subscribe Universal Event Handler Class
Create a univeral event handler class, which can be used to subscribe to any event type:
private class UniversalEventHandler : IEventHandler<object>
{
public void Handle(object eventData, AtataContext context)
{
// TODO: Implement.
}
}
Subscribe it during AtataContext building to different events:
AtataContext.GlobalConfiguration
.EventSubscriptions.Add<DriverInitEvent>(new UniversalEventHandler())
.EventSubscriptions.Add<AtataContextDeInitEvent>(new UniversalEventHandler());
Built-in Events
AtataContext Events
AtataContextPreInitEvent- occurs beforeAtataContextinitialization.AtataContextInitStartedEvent- occurs whenAtataContextis started to initialize.AtataContextInitCompletedEvent- occurs whenAtataContextis initialized.AtataContextDeInitEvent- occurs whenAtataContextis deinitializing.AtataContextDeInitCompletedEvent- occurs whenAtataContextis deinitialized.
Driver Events
DriverInitEvent- occurs whenAtataContextdriver is initializing.DriverDeInitEvent- occurs whenAtataContextdriver is deinitializing.
PageObject Events
PageObjectInitEvent- occurs whenPageObject<TOwner>is started to initialize.PageObjectInitCompletedEvent- occurs whenPageObject<TOwner>is initialized.PageObjectDeInitEvent- occurs whenPageObject<TOwner>is deinitialized.
Artifact Events
ArtifactAddedEvent- occurs when an artifact file is saved.